Hi, Greetings from FWQRC……………..
Today’s topic is about how Quality professionals help organisations to deliver. We explain who they are and how they go about it

- Everyone in an organisation is responsible for quality – from the CEO to the intern. But not everyone can be a quality expert. It’s important to have people who can provide the knowledge, tools and guidance to help everyone else play their part in pursuing excellence.These people are called quality professionals. Their job is to make sure organisations deliver.
- Quality professionals come in many guises. Some are generalists, some are specialists. Many will have titles such as quality manager, quality engineer, quality director or assurance manager, while others deal with quality as part of a broader remit. Some are concerned with the delivery of products and services, while some are part of the leadership of an organisation. Some are employed in-house, while others work outside the organisations they deal with.
- What unites quality professionals is their dedication to protecting and strengthening their organisations by making sure that stakeholders’ needs are met – and ideally, that their expectations are exceeded.

What quality professionals do
To put quality at the heart of their organisations, quality professionals focus on three specific areas, or competencies:
- Strong governance: This starts with top management expressing a commitment to quality. Effective governance means making sure that the aims of management are crystal clear, that they reflect the requirements of stakeholders, and that the right people, policies and processes are in place to turn them into action.
- Proper assurance: This ensures that the policies and priorities that have been decided on are being carried out properly, and that whatever is being produced – whether it’s a product, service, or project – is meeting stakeholders’ needs.
- A culture of improvement: This means continually evaluating the organisation’s performance to improve efficiency, eliminate waste, reduce risk, respond to changes and create new opportunities.
The measure of a quality professional’s success is how well we
- Protect reputation: avoiding the potentially catastrophic risks of getting things wrong
- Enhance reputation: maximizing value for our customers and stakeholders
- Improve profitability: eliminating unnecessary cost and waste and growing revenue
- Drive change: contributing to the ongoing improvement of the organisation
Quality professionals are recognized by colleagues as
- Agents for change: transforming processes, behaviour and culture
- Guardians: protecting the business by identifying appropriate standards for business performance and assuring that they are met
- Collaborators: working closely with leaders and managers
- Leaders: creating, managing and improving the organisation’s business process systems
- Progressive: understanding the realities of managing organisations in dynamic environments
- Holistic: looking across business functions and hierarchies to advocate a broad process and customer-centric view of the organisation
- Professional at FWQRC: qualified by professional institute (CQI), the CQI, and bound by a rigorous code of conduct.
Thank you for viewing FWQRC blogs….
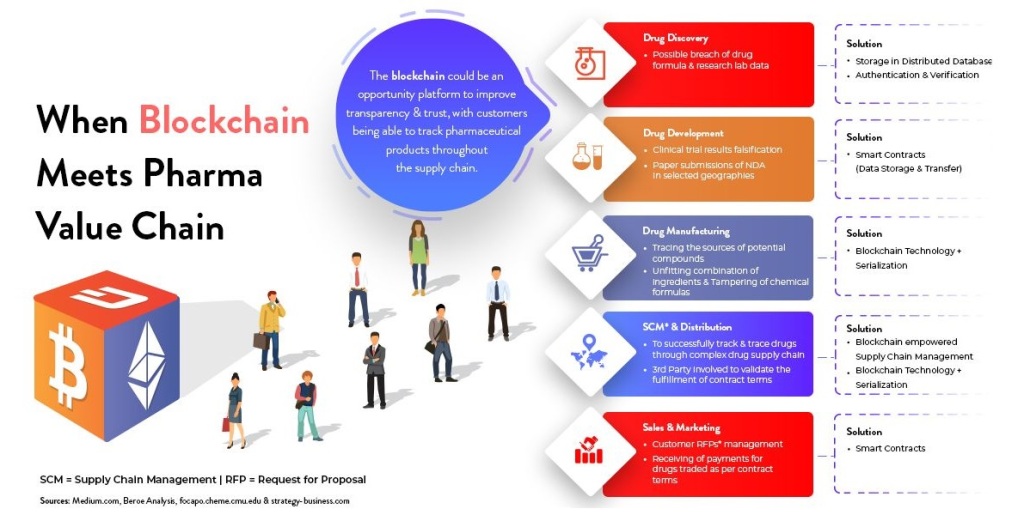
MITIGATING RISKS WITH BLACK CHAIN TECHNOLOGY
Hi, Greetings from FWQRC……….
This blog is related to how block chain contributes to drug supply management
WHAT IS BLOCK CHAIN?
Block chain, or a distributed ledger, is a way of organisation information is a way that gives all appropriate parties access to the information they need and keeps that information secure from people who should not see it
In terms of quality, block chains can ensure that every part of a supply chain can have assurance that the materials & products moving through it have reached a particular standard passed checks and compiled with necessary regulations
In its simple form,block chain is information that is shared across a group of computers so that if one person updates that information others are able to see it
HOW BLOCK CHAIN CONTRIBUTES TO DRUG SUPPLY-CHAIN MANAGEMENT
Imagine a simple supply chain: Company A produces raw material;company B makes it into a product,while company C sells it. With block chain,company A can alert company B & company C of changes in supply chain-such as overproduction-that they can then use to moderate their manufacturing process. Company B could extend their working hours and sales strategy, while company C could plan a marketing campaign to move the extra product
Sharing decentralized information in this way means that business relationships will become much more flexible,benefiting the participants and requiring no outside help. This can be a highly effective means of self regulation
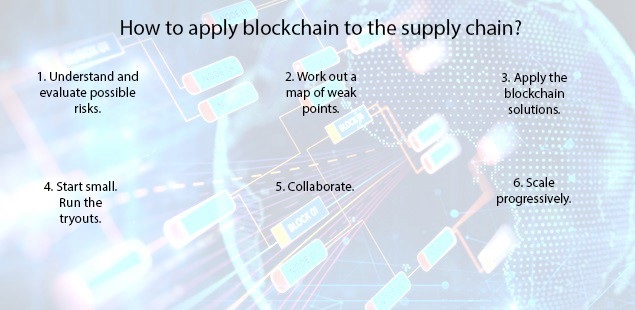
HOW BUSINESSES ARE USING BLOCK CHAIN IN THEIR SUPPLY CHAIN:
Global research firm, Gartner, predicts that by 2023,some 30% of manaufacturing complanies with revenue of more than $5bn will be using block chain to drive down costs and improve tracebility and transperancy
Block chain as a strategy will force companies to look beyond the boundaries of their own firm & establish shared process and consensus mechanisms with their supply chain partners
CHALLENGES OF THE MODEL
- The benefits are great,but they may come at a cost
- Block chain represents a challenge for businesses “Companies that have an ageing information technology infrastructure will struggle to interact effectively with digitally native companies
- Tech companies have a responsibility to make the user experience as easy & seamless as possible for everyone in the supply chain
Thank you for viewing FWQRC blogs……………………
Small Entity Compliance Guide (SECG)
February 3, 2020
The Food and Drug Administration today announced the availability of a Small Entity Compliance Guide (SECG) to help packaged food manufacturers meet federal standards in the final rule “ Food Labeling: Revision of the Nutrition and Supplement Facts Labels.” The final rule, which was published on May 27, 2016, amends the labeling regulations for foods and dietary supplements to provide updated nutrition information on the label to help consumers maintain healthy dietary practices.
The SECG is aimed at small businesses and restates, in plain language and in a question and answer format, the provisions in the final rule. It includes the following sections in addition to references:
Who is subject to the rule?
What foods are covered by the rule?
What foods are not covered by the rule?
Which nutrients must newly be declared, and what changes have been made to nutrients previously required or allowed to be declared?
How do I comply with recordkeeping requirements?
How have the values of nutrients been updated?
How do I comply with the formatting requirements?’
When must I comply with the rule?
Why must I comply with the rule?
Compliance with the updated Nutrition Facts labeling regulations was required by January 1, 2020, for manufacturers with $10 million or more in annual food sales, while manufacturers with less than $10 million in annual food sales will have an additional year to comply. During the first 6 months following the January 1, 2020, compliance date, FDA plans to work cooperatively with manufacturers to meet the new Nutrition Facts label requirements and will not focus on enforcement actions regarding these requirements during that time. FDA intends to exercise enforcement discretion to give manufacturers of single-ingredient sugars such as honey and maple syrup, and certain cranberry products, until July 1, 2021, to comply.
For Compliance,please write to fwqrcservices@gmail.com
Thank you for visiting FWQRC…
DEVELOPMENT OF A QUALITY CULTURE
Hi, Greetings from FWQRC……
Today’s topic is about the development of a Quality Culture and the supporting role of international standard development
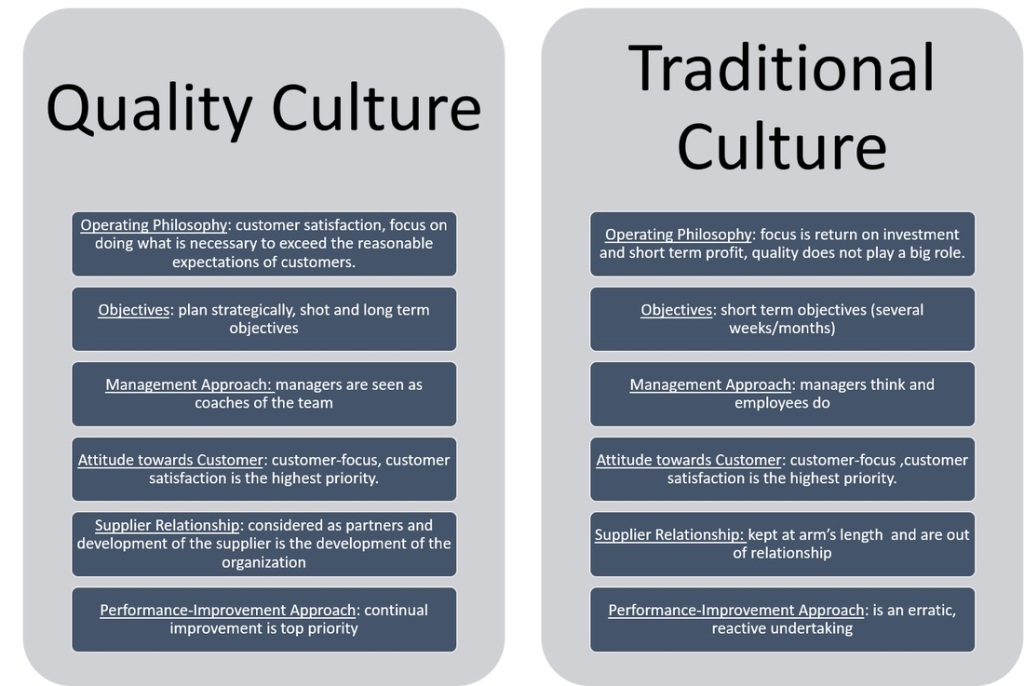
Quality Culture is a term being discussed with increasing regulatory among quality professionals as well as more widely outside of the quality profession, as organisations and governments consider continuous challenges including productivity, competitive strategy and reputation protection.Within a quality culture, everyone is involved in the ongoing pursuit of excellence

Each worker or team is both a supplier & customer within their organisation and takes responsibility for the quality of their output. In this setting, there is no need to check the final products as an incremental review has occurred on an ongoing basis at each stage
Conversely, the absence of a quality culture is likely to be characterized by an absence of individual or team responsibility and the need for costly & time consuming inspection and test regimes which add little value
Conclusion: Given the more elusive nature of culture compared to other facts of organisation life, it is not unreasonable for individuals to look for external sources of guidance. Assistance may be required to understand current culture, determine that culture which might best address requirements and to help define & deliver actions to support the quality culture journey.
Write to fwqrcservices@gmail.com to understand your organisations current culture, determine that culture and deliver actions to support the quality culture
FDA, USDA and EPA announce joint platform to streamline information about agricultural biotechnology products
Hi,Welcome to FWQRC Regulatory Focus News Letter…

Today, in recognition of January 2020 as National Biotechnology Month, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the Department of Agriculture and the Environmental Protection Agency launched a Unified Website for Biotechnology Regulation. The website streamlines information about the three regulatory agencies charged with overseeing agriculture biotechnology products and is part of President Donald J. Trump’s Executive Order on Modernizing the Regulatory Framework for Agricultural Biotechnology Products.
“This is a time of unprecedented scientific innovation. Agricultural biotechnology promises to bring dynamic new products to the marketplace,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, M.D. “At the FDA, we are committed to fostering flexible, risk-based approaches in this field while upholding our mission of protecting and promoting both human and animal health and animal well-being, for example by reducing their susceptibility to diseases like novel influenzas and resistance to zoonotic or foreign animal diseases. Our approach balances our internationally respected, science-based review standards with our ongoing risk-based regulatory approaches to ensure the safety of our food supply.”
The Unified Website for Biotechnology Regulation describes the federal review process for certain biotechnology products and allows users to submit questions to the three agencies. The goals of this website are to provide enhanced customer service to innovators and developers, while ensuring Americans continue to enjoy the safest and most affordable food supply in the world and can learn more about the safe use of biotechnology innovations.
In October 2018, the FDA announced its Plant and Animal Biotechnology Innovation Action Plan, which focuses on the agency’s risk-based regulatory approach. This approach will help secure confidence in the reliability and performance of plant and animal-based innovative products for consumers and America’s global trading partners. Making sure these products are safe is critical to maintaining consumer and commercial confidence in them and will help them to realize their full potential benefits for human and animal health.

The FDA uses a flexible, risk-based approach to the oversight of plant- and animal- derived products of biotechnology, focusing on safety and, where applicable, effectiveness. The agency’s approach includes, when appropriate, updating and clarifying science-based policies to support innovation and ensure that our regulatory processes are efficient, predictable, and proportionate to risk.
The FDA, an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, protects the public health by assuring the safety, effectiveness, and security of human and veterinary drugs, vaccines and other biological products for human use, and medical devices. The agency also is responsible for the safety and security of our nation’s food supply, cosmetics, dietary supplements, products that give off electronic radiation, and for regulating tobacco products.
Cosmetic Registration Reports

Hi, Welcome to FWQRC Regulatory Focus News Letter
About Blog FWQRC Regulatory focus pharma news, views and analysis of healthcare in a rapidly changing world. Not only do we keep you connected with the latest trends in pharma, we can also help you develop and bring to life your own thoughts, ideas and inspirations to enable you and your business to become key pharma influencers
The information in the tables below is a monthly report of activity in FDA’s Voluntary Cosmetic Registration Program (VCRP)
VCRP Monthly Status Report
Because the law does not require cosmetic firms to register their establishments or file their product formulations with FDA, participation in this program is voluntary. For this reason, the information below does not indicate the total number of companies manufacturing or marketing cosmetics in this country, or all cosmetic products on the market.
Activity for December 2019
- Number of online accounts activated this month: 103
- Number of products filed this month: 593
- Total activity since the launch of the new online system, September 20, 2018
- Number of active online accounts: 2,816
- Number of active cosmetic establishment registrations: 1,395
- Number of labelers that have filed product formulations*: 650
- Number of filed products: 8,333
- Number of product formulations discontinued**: 373
- Number of product formulations rejected***: 958
- Total activity since the VCRP was established, in 1972
- Number of active cosmetic establishment registrations: 4,392
- Number of labelers that have filed product formulations*: 3,071
- Number of active products on file: 68,838
- Number of product formulations discontinued**: 82,094
- Number of product formulations rejected***: 5,101

FWQRC™ intended to provide a decision pathway for drug & medical devices manufacturers in their first steps towards implementation of eCTD publishing and submission
Hi, Welcome to FWQRC™ Regulatory Focus News Letter
About Blog: FWQRC™ Regulatory focus pharma news, views and analysis of healthcare in a rapidly changing world. Not only do we keep you connected with the latest trends in pharma, we can also help you develop and bring to life your own thoughts, ideas and inspirations to enable you and your business to become key pharma influences
Many of us aware that eCTD is mandatory for DMF submissions from Jan 2020.
- At the beginning of the decision process it is very important to make an evaluation of the current submission processes (“where are we”) in comparison with the eCTD requirements (“where do we need to be”).
- The conclusions drawn from this analysis, together with a careful evaluation of the boundary conditions within the company are the basis for the definition of the User Requirements Specifications (URS).
- In the URS all the needs and boundaries of the expected processes are described and this information is used to find the optimal solution.Three possible solutions are described in detail, with their related advantages and disadvantages
- In-house software,
- Software as a Service (SaaS) and
- Outsourcing
- The last step of the process is the implementation of the chosen solution.
- It has to be considered whether a consultant should help with the creation of this URS document. Especially for the generation of the new processes the experience of a consultant can be helpfulThe URS is part of the official validation documentation according to GAMP and should be established for any new system
- Selection of solution
- Once the URS has been finalised, the most suitable solution has to be found. For this analysis the URS requirements should be classified in some way, e.g. “crucial” and “nice to have”.
- The three possible solutions (In-house Software, Software as a Service and Outsourcing) are described in detail in the following sections. Table 1 compares the most relevant characteristics of the 3 solutions, Table 2: Running an eCTD software system in-house: advantages and disadvantages and Table 3: Host system option: advantages and disadvantages
Table 1: Comparison of the 3 solutions
| Item | In-House software | Software as a Service | Outsourcing |
| Freedom of configuration | High | limited | No |
| Responsibility for update and Maintenance | High | No | No |
| IT support in-house needed | Yes | No | No |
| Link to other IT systems in-house possible | Yes | No | No |
| Initial costs | High | Low | No |
| Ongoing costs | In-house | Yes | Yes |
| Lead time | Long | Medium | Short |
| Scalability | Depends on set-up | Easy | Easy |
| Need of resources and competence for use of eCTD software | Yes | Yes | No |
| confidentiality / data security issues | No | Yes | Yes |
Table 2: Running an eCTD software system in-house: advantages and disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Full freedom for configuration | High initial costs for setting up the system |
| Free choice of hardware and software components | Relatively long lead time needed to set up the system |
| The software is part of the company-owned software and fits into the IT concept of the company | Full responsibility for update and maintenance |
| Everything stays in house (no data-transfer via internet / confidentiality etc.) | Personnel for technical set-up and maintenance must be available. |
| Link-up to other IT-systems possible (e.g. SAP) | |
| Maintenance costs stay in-house | |
| On-going costs are lower compared to the host software or outsourcing options |
Table 3: Host system option: advantages and disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Speed: time from the decision to a pilot eCTD is often shorter compared to the in-house software solution | Dependency on an external partner which increases if also the DMS shall be hosted |
| Lower cost for initial implementation as there is no or a smaller initial investment (e.g. initial set-up, user and software licenses, maintenance) | Data transfer via internet (confidentiality, upload / down load capacity) |
| Scalable: ability to scale as business needs change | Data hosted at an external company (confidentiality) |
| No on-going system maintenance | Limited freedom for software configuration |
| On-going costs for renting the system/service |
Table 4: Outsourcing option: advantages and disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Speed: time from the decision to a pilot eCTD is very short | Dependency on an external partner for each project and throughout the life cycle of a submission |
| No initial investment and no reoccurring costs for system maintenance and technical support | On-going costs for each service during the whole lifecycle of a product/submission (initial submission(s), variations etc.) |
| No direct costs for software, licenses, hardware, system validation and maintenance, training | Data transfer (confidentiality, upload / down load capacity) |
| No need to establish, maintain technical knowledge in building and publishing eCTDs, no need for respective in-house resources (eCTD builder/publisher) | Data hosted at an external company (confidentiality) |
| Scalable: ability to scale as business needs change | |
| Can also substantially-reduce risk of failed initial submissions |
- There are 4 main scenarios that can drive the decision for outsourcing
- there is no in-house software available to build / publish eCTDs or
- the in-house capacities are too little
- to gain experience for the creation of eCTD ready documents and eCTD submissions in-house
- the number of eCTD submissions is too small, seldom use of the system
- Conclusion: The option with the lowest impact on processes and systems in a company is outsourcing. There are various different extents of outsourcing. Common to all is that the external partner will provide the necessary infrastructure / software as well as the personnel to prepare the eCTD.
Stay in connected with FWQRC™ for implementation of eCTD publishing & submission